Are you experiencing knee pain, a common discomfort that can affect people of all ages? Let us help you to understand it better and navigate through this discomfort.
It often begins as a slight ache but can develop into a condition that significantly impacts your quality of life.
Knee pain is a very common discomfort some people feel across ages. It can start as slight discomfort and may progress into a condition that impairs the quality of living.
This detailed blog will focus on professional recommendations and natural measures to assist you handle knee pains better hence enhancing your overall wellbeing.
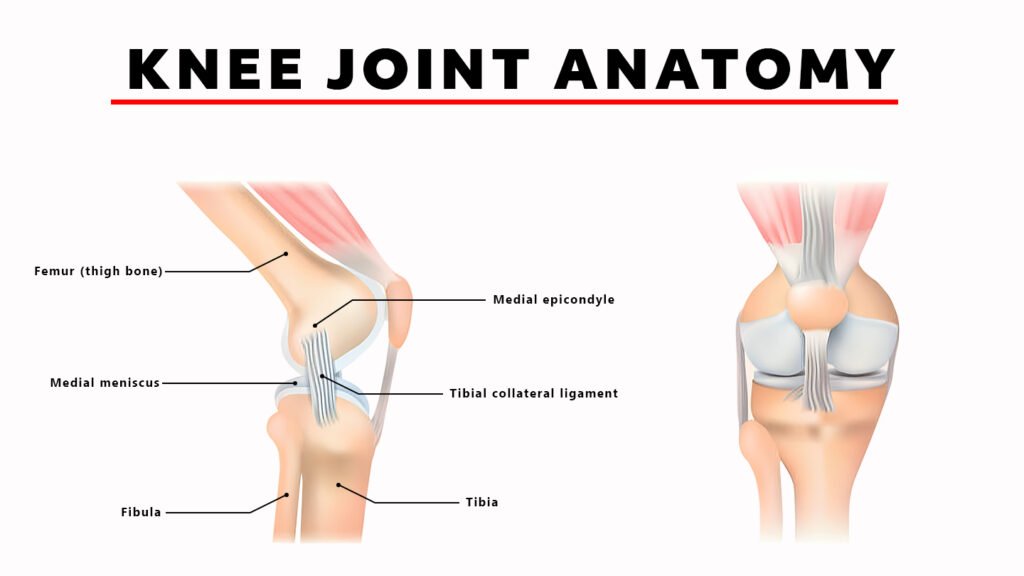
Understanding Knee Pain
Knee pain can differ in severity or intensity, and consequently can be located at the precise position within the knee-joint region or it may radiate all over it’s whole surface. This symptom can result by different factors which include accidents, diseases and life’s daily chores. The first step to relief from the ailment lies within understanding its origins.
Different Forms of Pain:
1. Acute Pain: This type occurs suddenly because of injury or trauma. It is characterized by high intensity but tends not to persist for long time periods.
2. Chronic Pain: In most cases chronic knee pain results from predisposing factors such as arthritis where it lingers on for several
weeks/months/years.
3. Referred Pain: Knee hurts because another joint or source such as lumbar spine or hip joint.
What causes a knee pain?
There are many reasons why people experience knee pain but every individual case is unique depending on various factors such as age, activity level, body weight and underlying health conditions among others. Therefore, it is important for patients with joint problems to consult their doctors if the pain persists for long or doesn’t reduce on self care.
Common Causes of Knee Pain:
A thorough comprehension of the main underlying cause of knee pain is
fundamental in providing the most effective treatment plans. Here are some
commonly known reasons:
Injuries
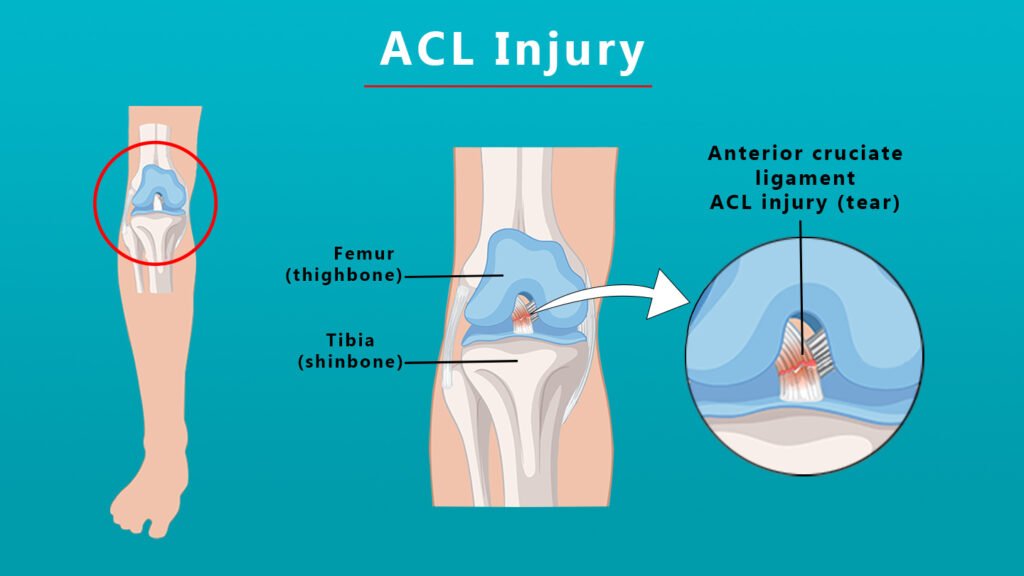
◆ Ligament injuries – Ligament injuries such as anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears mostly occur during sports and may present with significant destruction and instability associated with pain.
◆ Meniscus tears – The meniscus is a cartilage located between femur and tibia acting as a cushion; it can tear due to sudden twists when performing physical activities (such as dance or gymnastics) or wear from degenerative changes like aging process.
Medical conditions
1. Osteoarthritis – Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that leads to the breakdown of cartilage in the knee resulting in pain, stiffness, and swelling.
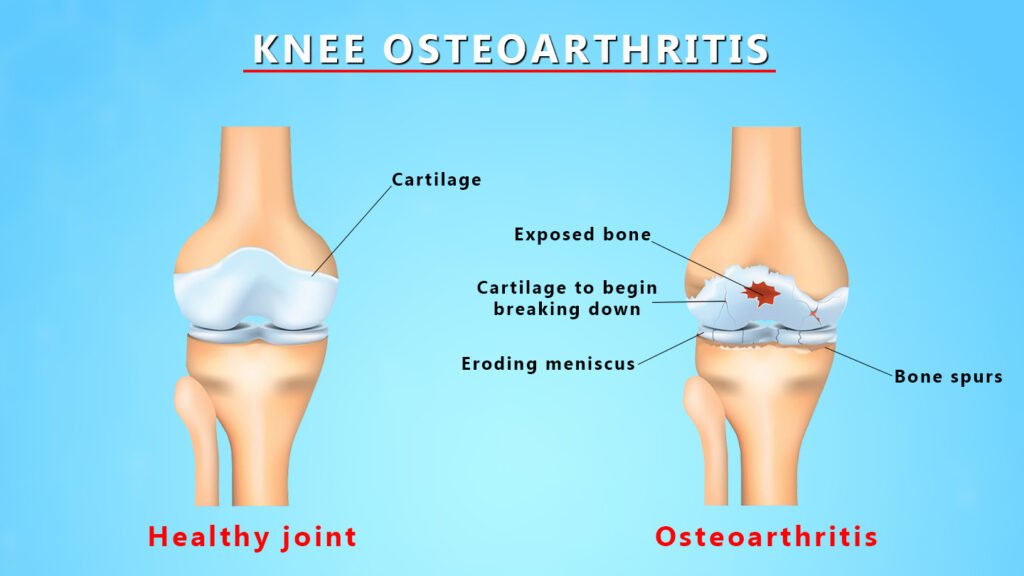
2. Rheumatoid arthritis – This autoimmune disease that brings about inflammation in the knee joint hence causing pain and eventually destruction over time.
3. Gouty arthritis – A type of arthritis brought on by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in joints which are extremely painful then inflamed.
4. Bursitis – Inflammation or swelling of small fluid-filled sacs situated near the knees known as bursae due to constant movement or pressure on the affected site.
Overuse and Mechanical Problems
1. Patellar tendinitis – It’s a condition also called jumper’s knee associated with excessive jumpers or runners efforts leading towards excessive involvement of your tendons surrounding patella gradually drying out until they become frayed or torn entirely
2. Iliotibial band syndrome -It is another common ailment seen among runners where there’s inflammation within an iliotibial band (a long piece of connective tissue stretching from pelvis all along outer thigh down).
How Knee Pain Affects Activities of Daily Living (ADLs)
Knee pain can create considerable difficulties in
completing Activities of Daily Living (ADLs).
Long term knee pain significantly reduces independence in ADLs, including:
■ Walking and Mobility: Daily activities like going to the washroom, walking in the park, and moving around the home become difficult and painful.
■ Sitting for long- Simple, sitting on a chair for a while, and getting up is painful for those who have a knee pain.
■ Physical activities and exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity is crucial for maintaining good health. Knee pain can decrease the ability to exercise, resulting in a reduction in cardiovascular strength, and leading to muscle atrophy and weight gain.
■ Taking care of personal hygiene: Activities like showering, grooming, and using the toilet require bending, squatting, and balancing, all of which can be affected by knee pain.
■ Household chores: Household chores such as cleaning, cooking and shopping require mobility and the ability to stand for long periods of time. Knee pain can make these tasks difficult and you may need help.
Risk factors of knee pain –
■ Excess weight
As weight-bearing joints, the knees are designed to support the body weight within limits. Excess weight put more stress on your joints, and that stress can lead to injury.

■ Previous knee injury
If your knees have been injured in the past, they may have areas of weakness that can affect balance and flexibility, making you more prone to joint injuries.
■ Sedentary lifestyle
Joints are designed to move. In fact, regular activity keeps natural lubricating fluids circulating and keeps joints healthy. When it comes to your joints, there is a saying that “use them or lose them” couldn’t be more accurate.
■ Certain types of jobs and sports
Knees are designed to bend and flex to support weight, but like any joint, they have natural limits. If you do activities that put a lot of stress on your knees, you are also more prone to knee injuries and chronic knee pain.
The activities that are most often responsible for
knee injuries include:
Ø Lifting weights
Ø Repetitive squats
Ø Jumping or running
Ø Quick changes in direction (turns)
Ø Spending a lot of time on your feet can also increase your risk of knee injuries, it is particularly significant when you stand in the same place for an extended time.
■ Wearing wrong shoes
Most people choose athletic shoes to improve sports performance. However, appropriate shoes also play a role in maintaining knee health. When selecting sports shoes, opt for those that offer adequate arch support, evenly distribute pressure, and provide ankle support.
Knee issues can result from various factors, not just sports shoes. Wearing high heels often increases the load on the
knee joint and disrupts its typical structural balance. Altering your natural balance also increases your risk of tripping, falls and injury.
Self-Care for Knee Pain
Effective self-care strategies can help manage knee pain and improve your quality of life. Here are some methods to consider:
Apply “POLICE” principle for acute injury
The Police Principle is a modern first aid technique for treating musculoskeletal injuries. POLICE is an acronym that represents Protection, Optimal Loading, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. This approach promotes safe and effective loading during the management of acute soft tissue injuries.
■ Protection-
■ Optimal Loading –
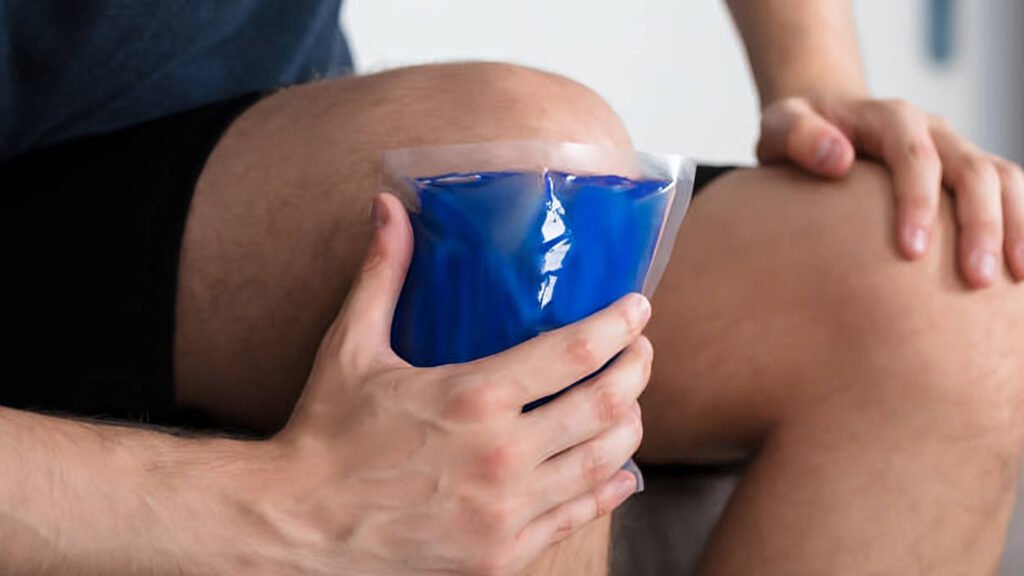
■ Ice therapy – Use ice packs to decrease inflammation
and alleviate pain.
Use ice for 15-20 minutes every 2-3 hours during the first 48 hours after an injury.
■ Compression- Use an elastic bandage or knee brace to provide support and reduce swelling.
■ Elevation- Elevate your knee above the level of your heart to reduce swelling.
Other self-care strategies -
◆ Rest and Activity Modification – Allow your knee to rest, especially after an injury or intense activity. Avoid activities that worsen the pain. Switch to low-impact activities like swimming or cycling that do not strain the knee as much.
◆Heat Therapy: Use heat packs or warm baths to relax muscles and improve blood flow, especially helpful for chronic pain.
◆Strengthening and Stretching Exercises-
➟ Strengthening Exercises: Focus on exercises that strengthen the muscles around your knee, such as leg lifts, squats, and lunges. Strong muscles offer improved support for the knee
joint.
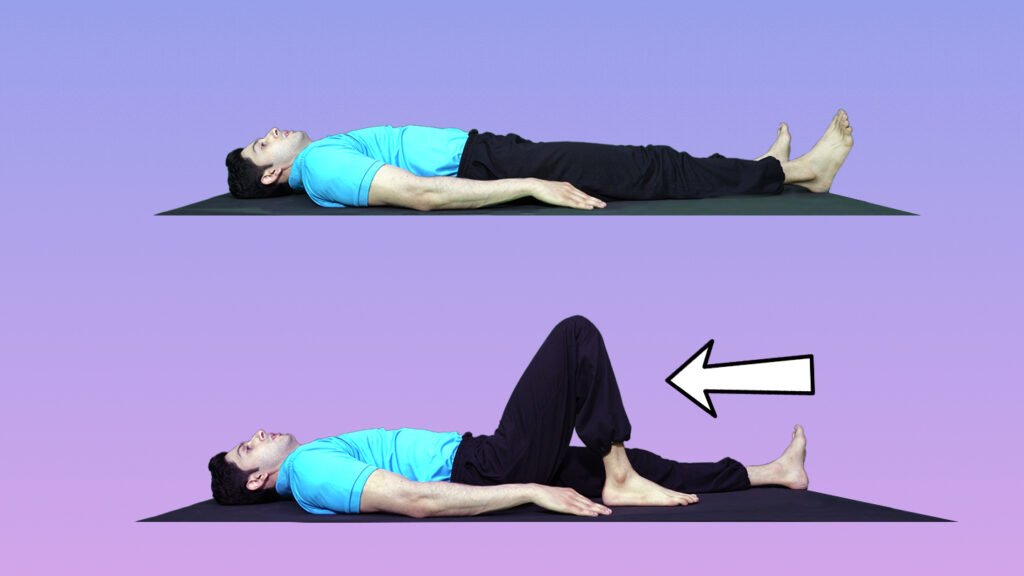
1. Heel slides
Position -Lie on your back with your legs extended and your feet slightly apart.
Movement – Slide your affected leg as close to your buttocks as you can.
Hold – Maintain this position for 5 seconds.
Slide your heel back to the starting position.
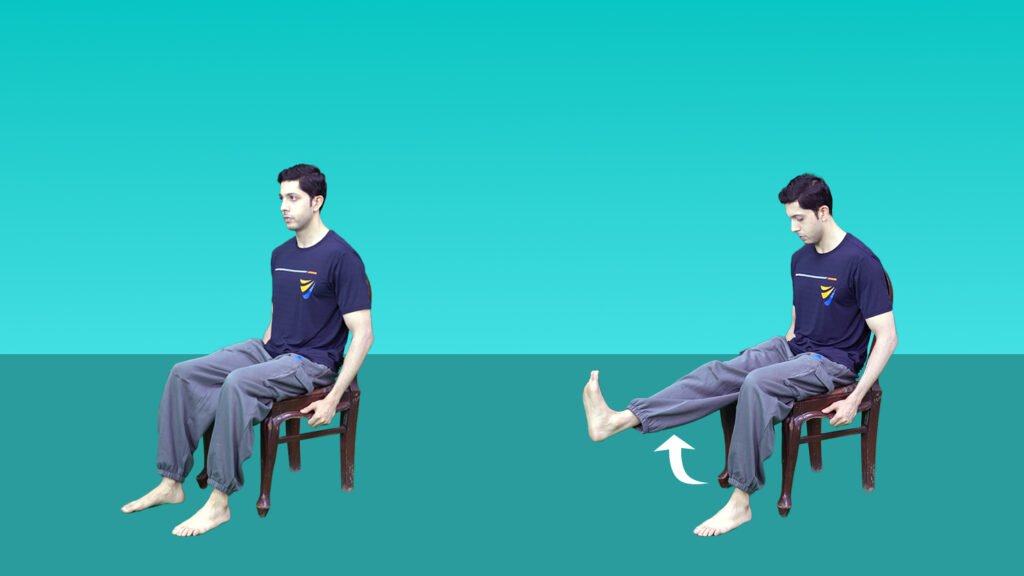
2. Dynamic quads
Position – Sit on a chair straight.
Movement – Extend your knee/ straighten up your leg.
Hold – Hold for 10 seconds and relax.
Repeat on the other side.

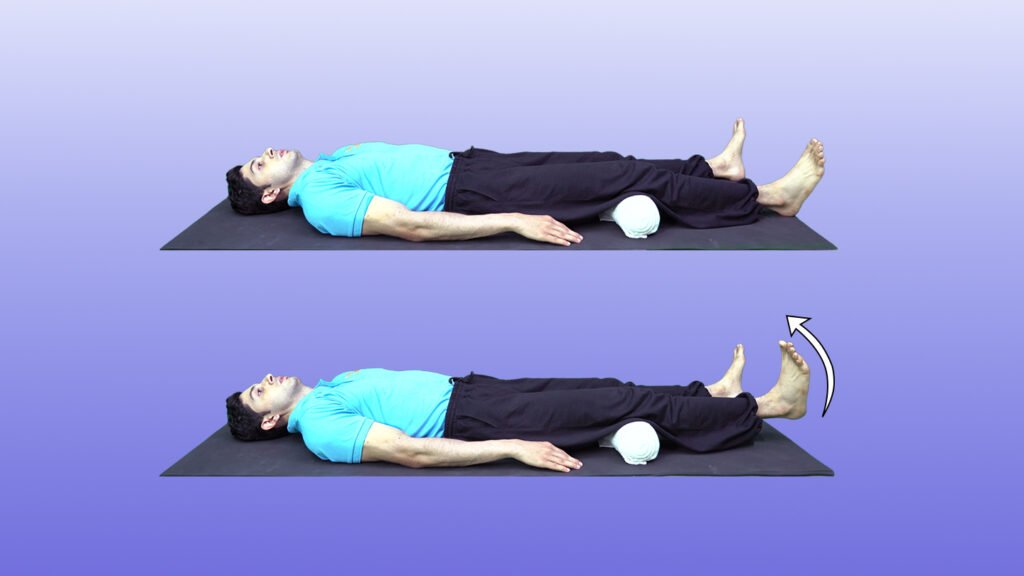
3. Knee extension over roll
Position – Place a rolled-up towel under one knee.
Movement – Press down on the towel as if straightening your knee. Pull
your toes and foot towards you to feel a stretch in your calf muscles,
allowing your heel to lift off the floor.
Hold – Hold for 5 seconds, thenrelax for 5 seconds.
➟ Stretching: Regular stretching of the hamstrings, quadriceps, and calves can improve flexibility and reduce
stiffness.
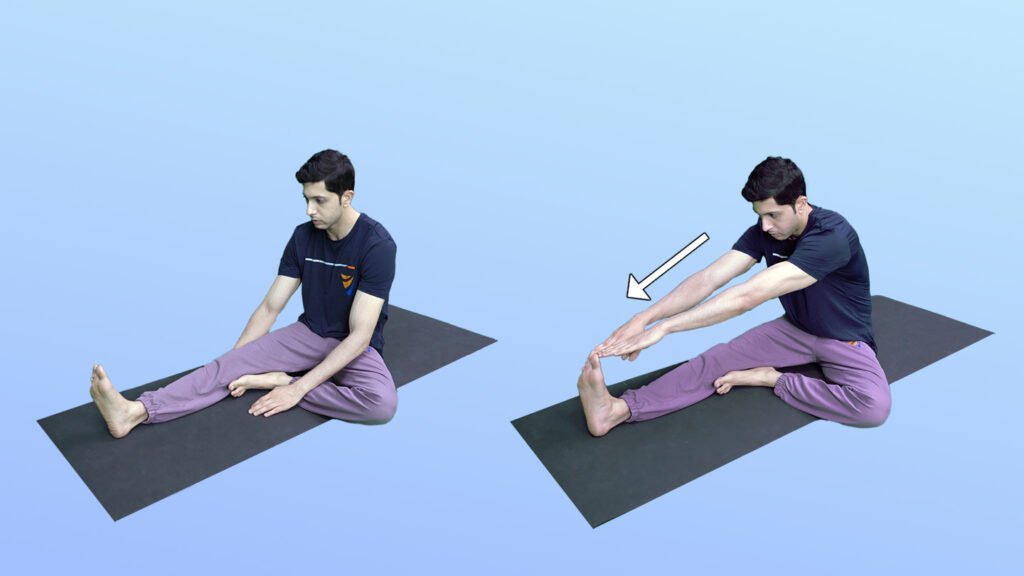
1. Seated hamstring stretch
Position – Sit on the floor with one leg straight in front of you and bend the other leg.
Movement – Lean forward from your hips, reaching towards your toes. Keep your back straight.
Hold -Hold for 20-30 seconds, then switch legs.

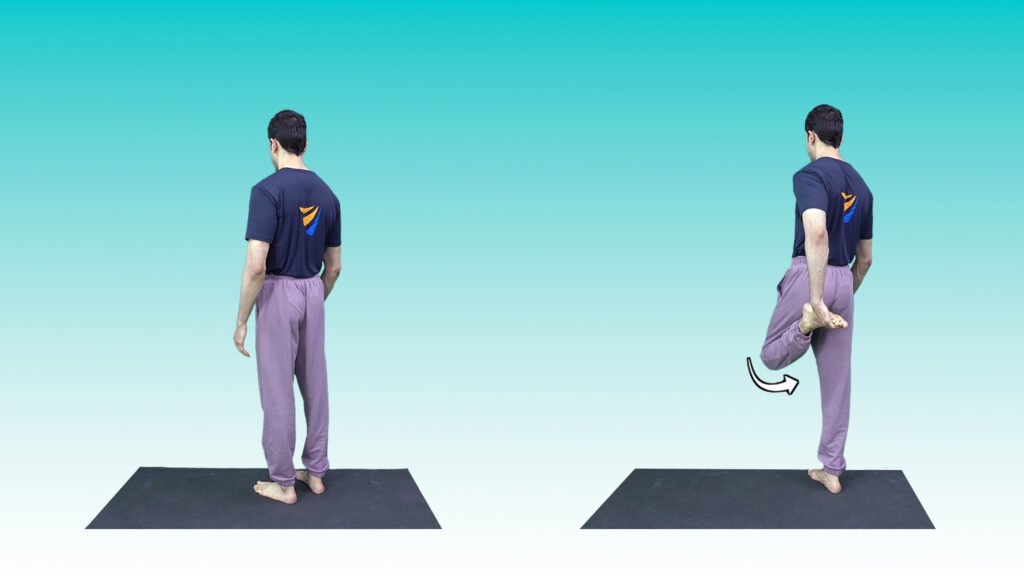
2. Standing quadriceps stretch
Position -Stand upright and hold onto a wall or chair for balance if needed.
Movement -Bend your right knee and bring your heel toward your buttocks, grabbing your ankle or foot with your right hand.
Stretch- Gently pull your heel closer to your buttocks until you feel a stretch along the front of your thigh.
Hold -Hold the stretch for 15-30 seconds, then switch legs and repeat on the other side.

3. Seated calf stretch with a towel
Position – Sit on the floor with your legs extended straight out in front of you. Wrap a towel or resistance band around the ball of one foot.
Movement- Hold the ends of the towel with both hands and gently pull the towel towards you. keep your leg straight and your foot flexed until you feel a stretch in your calf.
Hold –-hold the stretch for 20-30 seconds, then switch legs and repeat

◆ Weight Management – Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the strain on your knees. Even a small weight loss can significantly decrease knee pain.
◆ Proper Footwear – Wear shoes that provide good arch support and cushioning. Avoid wearing high heels and poorly fitting shoes.
Other Treatment Options:
When self-care measures are not enough, there are other treatment options to consider:
● Physiotherapy
A physiotherapist can create a customized exercise program to strengthen the muscles around your knee, improve flexibility, and enhance overall function. Techniques such as massage and joint mobilization can reduce pain and improve mobility.
● Dietary Changes to Support Knee Health –
✔ Fish
Salmon, mackerel, sardines, trout, and several other types of fish are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which are known to have anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce joint pain, stiffness, and arthritis symptoms. Eating fish also increases vitamin D levels in the body, which is lacking in people with arthritis.
✔ Olive Oil
Olive oil is a very good source of omega-3 fatty acids. This healthy fat reduces inflammation by 38.5%, and studies have shown that people who consume olive oil regularly have a lower risk of developing arthritis. Olive oil can be used in salad dressings and other dishes as a replacement for unhealthy fats.
✔ Nuts and Seeds
A serving of almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseeds, or pine nuts can provide the anti-inflammatory benefits you need to reduce pain and strengthen your joints. Add 1-2 ounces to a variety of dishes, including salads, rice bowls, and stir-fries. Berries: Strawberries, blueberries, blackberries, and other berries are packed with antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. Add a handful of your favourite berries to your smoothies or desserts for extra flavour and nutritional value.
✔ Leafy Greens
Cruciferous and leafy green vegetables, like cabbage, arugula, and spinach, are abundant in fiber, vitamins, and minerals that help block enzymes linked to inflammation.
✔ Ginger & Garlic
Ginger and garlic not only enhance flavour but also have other benefits like reducing inflammation and improving the immune system. In addition to being an ingredient in most knee pain relief products, it also improves heart health and reduces the risk of dementia.
✔ Turmeric
This spice is known to have many medicinal properties. Turmeric helps to reduce pain and other symptoms of osteoarthritis to a great extent. Indian cuisines are rich in turmeric as it is a base ingredient in most of the dishes.
✔ Green Tea
A cup of green tea is a convenient addition to treating disease symptoms and medication side effects. It contains polyphenolic compounds that exhibit anti-inflammatory properties and strengthen the immune system.
● Ointment -
Oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are effective for joint pains like knee pain, but they may also have some side effects. Prolonged use can frequently irritate the stomach lining and place strain on the kidneys.Fortunately, if you experience joint pain, there are other alternatives to consider. Topical creams, ointments, or gels may also be safe and effective substitutes for knee pain. One of the most common NSAID in ointment formulation is diclofenac.
Precautions:
While managing knee pain, it’s important to take certain precautions to avoid further injury or complications:
▶ Avoid High-Impact Activities – High-Impact Sports: Activities such as running, jumping, or intense aerobics can exacerbate knee pain. Opt for low-impact exercises instead.
▶ Avoid aggravating factors an activity causes pain, stop and rest. Ignoring pain can result in additional injuries.
▶ Gradual Increase: When starting a new exercise program, increase the intensity and duration gradually to avoid overloading your knee.
▶Use Assistive Devices-
1. Knee Braces: Wearing a knee brace can provide additional support and stability, especially during activities that put stress on the knee.
2. Walking Aids: Using a cane or crutches can help reduce the weight on
your knee and prevent further damage.
When Should I Consult a Medical Professional?
☑ Severe Pain – If you experience severe pain that does not improve with rest and self-care, consult a healthcare professional.
☑ Swelling and Redness – Sudden swelling, redness, or warmth around the knee could indicate an infection or other serious condition that requires medical attention.
☑ Inability to Bear Weight – If you cannot bear weight on your knee or feel instability, it’s important to get it evaluated by a professional.
☑ Deformity – Any visible deformity or misalignment of the knee joint should be assessed by a healthcare provider.
☑ Signs of Infection – fever and chills accompanied by knee pain, these symptoms could indicate an infection that requires prompt
medical treatment.
☑ Persistent Symptoms – Chronic Pain: If your knee pain persists for several weeks despite self-care efforts, it’s time to consult a professional for further evaluation and treatment options.
Conclusion:
Knee pain can be a challenging condition to live with, but with the right approach, it is possible to manage and alleviate discomfort. By incorporating expert advice and effective natural treatments into your routine, you can find relief and improve your quality of life. Remember, it’s essential to consult with healthcare professionals to tailor a treatment plan that addresses your specific needs and conditions. Stay proactive, stay informed, and take steps towards a pain-free life.